引言:二叉查找树的C++实现代码,并进行了测试。
二叉查找树简介
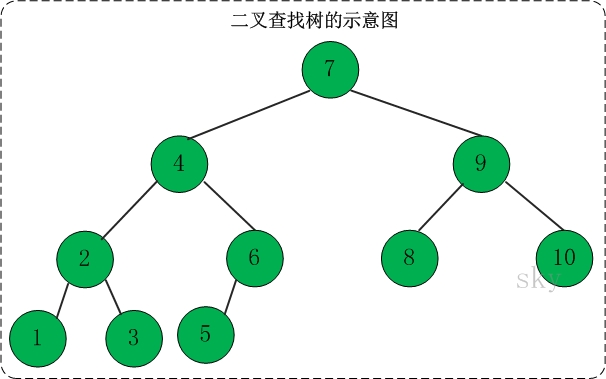
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),又被称为二叉搜索树。它是特殊的二叉树:对于二叉树,假设x为二叉树中的任意一个结点,x节点包含关键字key,节点x的key值记为key[x]。如果y是x的左子树中的一个结点,则key[y] <= key[x];如果y是x的右子树的一个结点,则key[y] >= key[x]。那么,这棵树就是二叉查找树。如下图所示:
在二叉查找树中:
(1)若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
二叉查找树的C++实现
节点和二叉查找树的定义
二叉查找树节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 template <class T >class BSTNode {public : T key; BSTNode* left; BSTNode* right; BSTNode* parent; BSTNode (T value, BSTNode *p, BSTNode *l, BSTNode *r): key (value),parent (p),left (l),right (r) {} }
BSTNode是二叉查找树的节点,它包含二叉查找树的几个基本信息:
(1)key – 它是关键字,是用来对二叉查找树的节点进行排序的;
二叉树操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 template <class T >class BSTree {private : BSTNode<T>* mRoot; public : BSTree (); ~BSTree (); void preOrder () void inOrder () void postOrder () BSTNode<T>* search (T key) ; BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch (T key) ; T minimum () ; T maximum () ; BSTNode<T>* successor (BSTNode<T> *x) ; BSTNode<T>* predecessor (BSTNode<T> *x) ; void insert (T key) void remove (T key) void destroy () void print () private : void preOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const void inOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const void postOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const BSTNode<T>* search (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const ; BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const ; BSTNode<T>* minimum (BSTNode<T>* tree) ; BSTNode<T>* maximum (BSTNode<T>* tree) ; void insert (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z) BSTNode<T>* remove (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z) ; void destroy (BSTNode<T>* &tree) void print (BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction) }
BSTree是二叉树。它包含二叉查找树的根节点和二叉查找树的操作。二叉查找树的操作中有许多重载函数,例如insert()函数,其中一个是内部接口,另一个是提供给外部的接口。
遍历
这里讲解前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历3种方式。
前序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(1)访问根结点;
前序遍历代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 template <class T >void BSTree<T>::preOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const { if (tree != NULL ) { cout<< tree->key << " " ; preOrder (tree->left); preOrder (tree->right); } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::preOrder () { preOrder (mRoot); }
中序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(1)中序遍历左子树;
中序遍历代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 template <class T >void BSTree<T>::inOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const { if (tree != NULL ) { inOrder (tree->left); cout<< tree->key << " " ; inOrder (tree->right); } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::inOrder () { inOrder (mRoot); }
后序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
(1)后序遍历左子树;
后序遍历代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 template <class T >void BSTree<T>::postOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const { if (tree != NULL ) { postOrder (tree->left); postOrder (tree->right); cout<< tree->key << " " ; } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::postOrder () { postOrder (mRoot); }
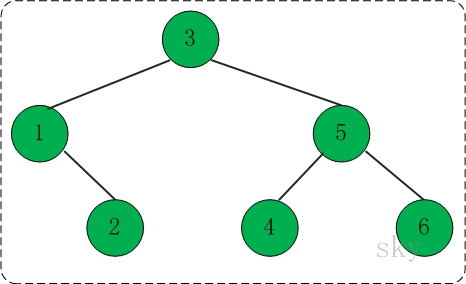
看看下面这颗树的各种遍历方式:
对于上面的二叉树而言,
查找
递归版本的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const { if (x==NULL || x->key==key) return x; if (key < x->key) return search (x->left, key); else return search (x->right, key); } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search (T key) { search (mRoot, key); }
非递归版本的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const { while ((x!=NULL ) && (x->key!=key)) { if (key < x->key) x = x->left; else x = x->right; } return x; } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch (T key) { iterativeSearch (mRoot, key); }
最大值和最小值
查找最大值的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::maximum (BSTNode<T>* tree) { if (tree == NULL ) return NULL ; while (tree->right != NULL ) tree = tree->right; return tree; } template <class T >T BSTree<T>::maximum () { BSTNode<T> *p = maximum (mRoot); if (p != NULL ) return p->key; return (T)NULL ; }
查找最小值的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::minimum (BSTNode<T>* tree) { if (tree == NULL ) return NULL ; while (tree->left != NULL ) tree = tree->left; return tree; } template <class T >T BSTree<T>::minimum () { BSTNode<T> *p = minimum (mRoot); if (p != NULL ) return p->key; return (T)NULL ; }
前驱和后继
节点的前驱:是该节点的左子树中的最大节点。
查找前驱节点的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::predecessor (BSTNode<T> *x) { if (x->left != NULL ) return maximum (x->left); BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent; while ((y!=NULL ) && (x==y->left)) { x = y; y = y->parent; } return y; }
查找后继节点的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::successor (BSTNode<T> *x) { if (x->right != NULL ) return minimum (x->right); BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent; while ((y!=NULL ) && (x==y->right)) { x = y; y = y->parent; } return y; }
插入
插入节点的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 template <class T >void BSTree<T>::insert (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z) { BSTNode<T> *y = NULL ; BSTNode<T> *x = tree; while (x != NULL ) { y = x; if (z->key < x->key) x = x->left; else x = x->right; } z->parent = y; if (y==NULL ) tree = z; else if (z->key < y->key) y->left = z; else y->right = z; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::insert (T key) { BSTNode<T> *z=NULL ; if ((z=new BSTNode<T>(key,NULL ,NULL ,NULL )) == NULL ) return ; insert (mRoot, z); }
删除
删除节点的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::remove (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z) { BSTNode<T> *x=NULL ; BSTNode<T> *y=NULL ; if ((z->left == NULL ) || (z->right == NULL ) ) y = z; else y = successor (z); if (y->left != NULL ) x = y->left; else x = y->right; if (x != NULL ) x->parent = y->parent; if (y->parent == NULL ) tree = x; else if (y == y->parent->left) y->parent->left = x; else y->parent->right = x; if (y != z) z->key = y->key; return y; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::remove (T key) { BSTNode<T> *z, *node; if ((z = search (mRoot, key)) != NULL ) if ( (node = remove (mRoot, z)) != NULL ) delete node; }
打印
打印二叉查找树的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 template <class T >void BSTree<T>::print (BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction) { if (tree != NULL ) { if (direction==0 ) cout << setw (2 ) << tree->key << " is root" << endl; else cout << setw (2 ) << tree->key << " is " << setw (2 ) << key << "'s " << setw (12 ) << (direction==1 ?"right child" : "left child" ) << endl; print (tree->left, tree->key, -1 ); print (tree->right,tree->key, 1 ); } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::print () { if (mRoot != NULL ) print (mRoot, mRoot->key, 0 ); }
销毁
销毁二叉查找树的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 template <class T >void BSTree<T>::destroy (BSTNode<T>* &tree) { if (tree==NULL ) return ; if (tree->left != NULL ) return destroy (tree->left); if (tree->right != NULL ) return destroy (tree->right); delete tree; tree=NULL ; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::destroy () { destroy (mRoot); }
二叉查找树的C++实现(完整源码)
二叉查找树的C++实现文件(BSTree.h)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 #ifndef _BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_HPP_ #define _BINARY_SEARCH_TREE_HPP_ #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> using namespace std;template <class T >class BSTNode { public : T key; BSTNode *left; BSTNode *right; BSTNode *parent; BSTNode (T value, BSTNode *p, BSTNode *l, BSTNode *r): key (value),parent (),left (l),right (r) {} }; template <class T >class BSTree { private : BSTNode<T> *mRoot; public : BSTree (); ~BSTree (); void preOrder () void inOrder () void postOrder () BSTNode<T>* search (T key) ; BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch (T key) ; T minimum () ; T maximum () ; BSTNode<T>* successor (BSTNode<T> *x) ; BSTNode<T>* predecessor (BSTNode<T> *x) ; void insert (T key) void remove (T key) void destroy () void print () private : void preOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const void inOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const void postOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const BSTNode<T>* search (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const ; BSTNode<T>* iterativeSearch (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const ; BSTNode<T>* minimum (BSTNode<T>* tree) ; BSTNode<T>* maximum (BSTNode<T>* tree) ; void insert (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z) BSTNode<T>* remove (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z) ; void destroy (BSTNode<T>* &tree) void print (BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction) }; template <class T >BSTree<T>::BSTree ():mRoot (NULL ) { } template <class T >BSTree<T>::~BSTree () { destroy (); } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::preOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const { if (tree != NULL ) { cout<< tree->key << " " ; preOrder (tree->left); preOrder (tree->right); } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::preOrder (){ preOrder (mRoot); } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::inOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const { if (tree != NULL ) { inOrder (tree->left); cout<< tree->key << " " ; inOrder (tree->right); } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::inOrder (){ inOrder (mRoot); } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::postOrder (BSTNode<T>* tree) const { if (tree != NULL ) { postOrder (tree->left); postOrder (tree->right); cout<< tree->key << " " ; } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::postOrder (){ postOrder (mRoot); } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const { if (x==NULL || x->key==key) return x; if (key < x->key) return search (x->left, key); else return search (x->right, key); } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::search (T key) { search (mRoot, key); } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch (BSTNode<T>* x, T key) const { while ((x!=NULL ) && (x->key!=key)) { if (key < x->key) x = x->left; else x = x->right; } return x; } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::iterativeSearch (T key) { iterativeSearch (mRoot, key); } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::minimum (BSTNode<T>* tree) { if (tree == NULL ) return NULL ; while (tree->left != NULL ) tree = tree->left; return tree; } template <class T >T BSTree<T>::minimum () { BSTNode<T> *p = minimum (mRoot); if (p != NULL ) return p->key; return (T)NULL ; } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::maximum (BSTNode<T>* tree) { if (tree == NULL ) return NULL ; while (tree->right != NULL ) tree = tree->right; return tree; } template <class T >T BSTree<T>::maximum () { BSTNode<T> *p = maximum (mRoot); if (p != NULL ) return p->key; return (T)NULL ; } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::successor (BSTNode<T> *x) { if (x->right != NULL ) return minimum (x->right); BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent; while ((y!=NULL ) && (x==y->right)) { x = y; y = y->parent; } return y; } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::predecessor (BSTNode<T> *x) { if (x->left != NULL ) return maximum (x->left); BSTNode<T>* y = x->parent; while ((y!=NULL ) && (x==y->left)) { x = y; y = y->parent; } return y; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::insert (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T>* z){ BSTNode<T> *y = NULL ; BSTNode<T> *x = tree; while (x != NULL ) { y = x; if (z->key < x->key) x = x->left; else x = x->right; } z->parent = y; if (y==NULL ) tree = z; else if (z->key < y->key) y->left = z; else y->right = z; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::insert (T key){ BSTNode<T> *z=NULL ; if ((z=new BSTNode<T>(key,NULL ,NULL ,NULL )) == NULL ) return ; insert (mRoot, z); } template <class T >BSTNode<T>* BSTree<T>::remove (BSTNode<T>* &tree, BSTNode<T> *z) { BSTNode<T> *x=NULL ; BSTNode<T> *y=NULL ; if ((z->left == NULL ) || (z->right == NULL ) ) y = z; else y = successor (z); if (y->left != NULL ) x = y->left; else x = y->right; if (x != NULL ) x->parent = y->parent; if (y->parent == NULL ) tree = x; else if (y == y->parent->left) y->parent->left = x; else y->parent->right = x; if (y != z) z->key = y->key; return y; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::remove (T key){ BSTNode<T> *z, *node; if ((z = search (mRoot, key)) != NULL ) if ( (node = remove (mRoot, z)) != NULL ) delete node; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::destroy (BSTNode<T>* &tree){ if (tree==NULL ) return ; if (tree->left != NULL ) return destroy (tree->left); if (tree->right != NULL ) return destroy (tree->right); delete tree; tree=NULL ; } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::destroy (){ destroy (mRoot); } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::print (BSTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction){ if (tree != NULL ) { if (direction==0 ) cout << setw (2 ) << tree->key << " is root" << endl; else cout << setw (2 ) << tree->key << " is " << setw (2 ) << key << "'s " << setw (12 ) << (direction==1 ?"right child" : "left child" ) << endl; print (tree->left, tree->key, -1 ); print (tree->right,tree->key, 1 ); } } template <class T >void BSTree<T>::print (){ if (mRoot != NULL ) print (mRoot, mRoot->key, 0 ); } #endif
关于二叉查找树的C++实现有两点需要补充说明的:第2点:将二叉查找树的"声明"和"实现"都位于BSTree.h中。这是因为,在二叉查找树的实现采用了模板;而C++编译器不支持对模板的分离式编译!
二叉查找树的C++测试程序
二叉查找树的C++测试程序(BSTreeTest.cpp)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 #include <iostream> #include "BSTree.h" using namespace std;static int arr[]= {1 ,5 ,4 ,3 ,2 ,6 };#define TBL_SIZE(a) ( (sizeof(a)) / (sizeof(a[0])) ) int main () int i, ilen; BSTree<int >* tree=new BSTree<int >(); cout << "== 依次添加: " ; ilen = TBL_SIZE (arr); for (i=0 ; i<ilen; i++) { cout << arr[i] <<" " ; tree->insert (arr[i]); } cout << "\n== 前序遍历: " ; tree->preOrder (); cout << "\n== 中序遍历: " ; tree->inOrder (); cout << "\n== 后序遍历: " ; tree->postOrder (); cout << endl; cout << "== 最小值: " << tree->minimum () << endl; cout << "== 最大值: " << tree->maximum () << endl; cout << "== 树的详细信息: " << endl; tree->print (); cout << "\n== 删除根节点: " << arr[3 ]; tree->remove (arr[3 ]); cout << "\n== 中序遍历: " ; tree->inOrder (); cout << endl; tree->destroy (); return 0 ; }
运行结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 == 依次添加: 1 5 4 3 2 6 == 前序遍历: 1 5 4 3 2 6 == 中序遍历: 1 2 3 4 5 6 == 后序遍历: 2 3 4 6 5 1 == 最小值: 1 == 最大值: 6 == 树的详细信息: 1 is root 5 is 1' s right child 4 is 5' s left child 3 is 4' s left child 2 is 3' s left child 6 is 5' s right child == 删除根节点: 3 == 中序遍历: 1 2 4 5 6
下面对测试程序的流程进行分析!
(1)新建"二叉查找树"root。
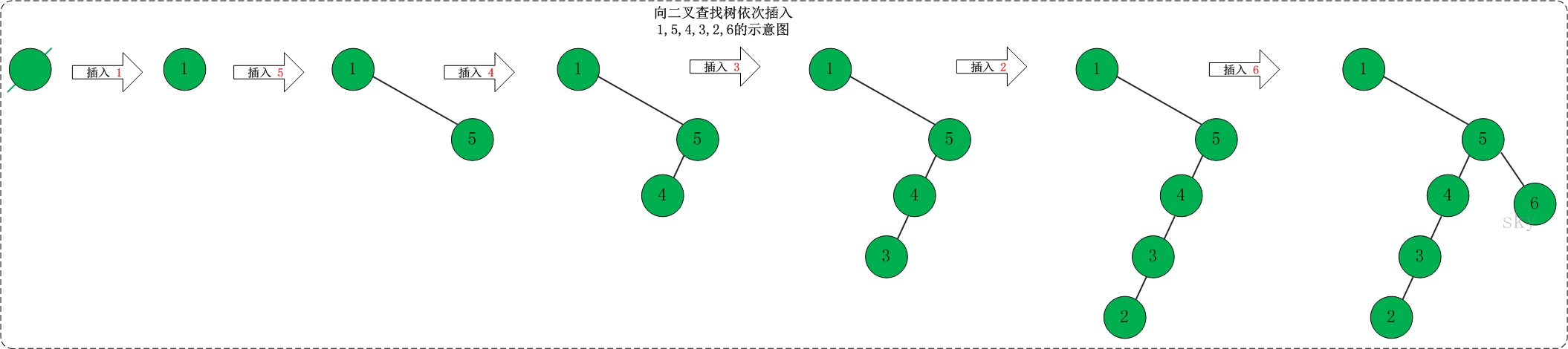
(2)向二叉查找树中依次插入1,5,4,3,2,6 。如下图所示:
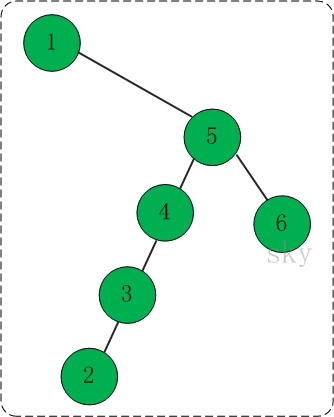
(3)遍历和查找,插入1,5,4,3,2,6之后,得到的二叉查找树如下:
前序遍历结果: 1 5 4 3 2 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 6 5 1
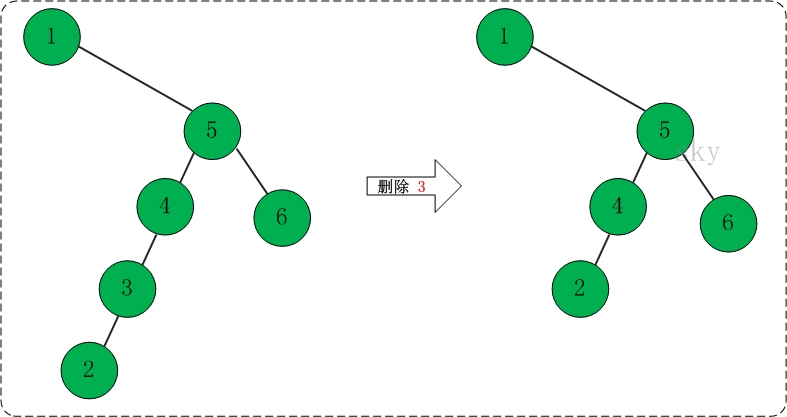
(4)删除节点3。如下图所示:
(5)重新遍历该二叉查找树。1 2 4 5 6
总结
二叉查找树的C++实现代码,并进行了测试。
本文转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3576373.html